Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohno, Shuji; Matsuki, Takuo*; ; Miyake, Osamu
JNC TN9520 2000-001, 196 Pages, 2000/01
ASSCOPS (Analysis of Simultaneous Sodium Combustion in Pool and Spray) has been developed for analyses of thermal consequences of sodium leak and fire accidents in LMFBRs. This report presents a description of the computational models, input and output data as the user's manual of ASSCOPS version 2.1. ASSCOPS is an integrated computational code based on the sodium pool fire code SOFIRE II developed by the Atomics International Division of Rockwell International, and on the sodium spray fire code SPRAY developed by the Hanford Engineering Development Laboratory in the U.S. The users of ASSCOPS need to specify the sodium leak conditions (leak flow rate and temperature, etc.), the cell geometries (cell volume, surface area and thickness of structures, etc.), and the atmospheric initial conditions such as gas temperature, pressure, and composition. ASSCOPS calculates the time histories of atmospheric temperature, pressure and of structural temperature.
Takemura, Morio*
PNC TJ9055 97-001, 112 Pages, 1997/03
With use of a standard groupwise shielding design library JSSTDL produced from the latest evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-3.2, experimental analyses for the Axial Shield Experiment (homogeneous and central blockage type shield configurations with B C or stainless steel shield material) were performed. The results were compared with those obtained by the same analysis method and input data using JSDJ2 library that had been applied consistently to the JASPER experiment analyses. In general, the results with JSSTDL analyses are higher than those by JSDJ2 as were found in analyses in last year for the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment and the Special Materials Experiment. Consideration was made on the discrepancies between JSSTDL and JSDJ2 analysis results of the Axial Shield Experiment and also those of the sodium configulation in the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment. The former was done by exchange of macro cross section of each region, and the latter forcused on sodium cross section was done with use of cross section sensitivity analysis method. Compilation of the input data necessary for future reanalyses of important configurations in JASPER experiments, that were selected in previous study in last year, were continued and new data were added into the computer disk holding previous ones.
C or stainless steel shield material) were performed. The results were compared with those obtained by the same analysis method and input data using JSDJ2 library that had been applied consistently to the JASPER experiment analyses. In general, the results with JSSTDL analyses are higher than those by JSDJ2 as were found in analyses in last year for the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment and the Special Materials Experiment. Consideration was made on the discrepancies between JSSTDL and JSDJ2 analysis results of the Axial Shield Experiment and also those of the sodium configulation in the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment. The former was done by exchange of macro cross section of each region, and the latter forcused on sodium cross section was done with use of cross section sensitivity analysis method. Compilation of the input data necessary for future reanalyses of important configurations in JASPER experiments, that were selected in previous study in last year, were continued and new data were added into the computer disk holding previous ones.
Kawasaki, Nobuchika; kasahara, Naoto
PNC TN9410 96-294, 47 Pages, 1996/07
As main components of fast reactors, there are reactor vessels, pipes, heat exchangers, nozzles. In order to keep their structural integrity, the elevated temperature structural design guide evaluates primary stress, strain, and creep-fatigue damage of them. Especially in fast reactors which operate under low pressure and high temperature conditions, creep-fatigue damage is dominant, and limits a design range. For the purpose of extending a design range, author evaluated strength of cylindrical structures by an advanced proposed method based on the generalized elastic follow-up model. Furthermore we studied evaluation accuracy of a method of 'monjyu" and a proposed method, through comparison of thermal transient strength test data with damage calculated by two strength evaluation methods. Results are summarized as follows. (1)An advanced proposed method predicted lower fatigue damage (Df) than a method of 'monjyu'. (However, in structural discontinuities where an elastic follow up is large, a proposed method shows higher damage than a method of 'monjyu'.) (2)An advanced proposed method calculated lower creep damage (Dc) than a method of 'monjyu'. (About 0.7 times lower in a cylindrical structure with a structural discontinuity (STF-3). About 0.1 times lower in a cylindrical structure without a structural discontinuity (STF-10). (3)On no-crack portions in STF-3, prediction of a method of 'monjyu' is out of a limit of crack initiation, nevertheless one of an advanced proposed method is within the range. Through above results, an advanced proposed method was evaluated to be more accurate in prediction of creep-fatigue damage. We concluded from the above investigation that we calculated more rational and lower damage by proposed method, and it has the possibilities to get extension of a design range.
*;
PNC TN9410 96-102, 40 Pages, 1996/04
In designing the shield plug of LMFBR, it is important to evaluate the thermal response between the cover gas thermal-hydraulics and the temperature fields of the shield plug at the same time. Based on the experiments which were performed by OEC, the natural convection and the thermal radiation in the cover gas layer were calculated with the structure simulating the shield plug in a detail two-dimensional model. The calculations were carried out for 8 kinds of experimental RUNs using a FLUSH code. The main results were as follows: (1)For these 8 kinds of experimental RUNs, the velocity and the temperature distributions in the cover gas layer were presented. The radial and axial temperature distributions in the rotating plug were also presented, which were difficult to measure by the experiments. (2)The boundary surface temperature between the cover gas layer and the rotating plug had the same tendencies and the calculated average temperatures on the boundary surface had good agreements with the experimental data. The average relative deviations from experimental values were less than 1.3%. (3)The natural convection of the cover gas enhanced the temperature distributions in the structure. The effects of thermal radiation on the heat transfer was relatively small and it can be neglected when the temperature of the heated aluminum disk is less than 400 C.
C.
kasahara, Naoto
PNC TN9520 93-009, 223 Pages, 1993/04
None
Chatani, Keiji; ; ; Masui, Tomohiko*; Nagai, Akinori; ;
PNC TN9410 92-186, 63 Pages, 1992/06
Dose rates around UGT (Upper Guide Tube) of CRDM (Control Rod Drive Mechanism) have been measured in Experimental Fast Reactor "JOYO" during the 9th periodical inspection in order to reflect the study on the shield thickness of UIS (Upper Internal Structure) cask, which has been planned to be used for a Large Fast Reactor. Absolute amount of radioactive corrosion products (CP) is evaluated by gamma spectra analysis for waste water from cleaned UGT. The results on this study are summarized as follows: (1)Measured dose rates distribution around UGT before and after clean-up show the same reduction. The affection of CP is not clearly observed for the dose rate distribution. (2)The relative values of dose rate, which are evaluated by considering the inside structure of UGT, show the attenuation of 10 from bottom to sodium level of UGT. The above relative distribution agrees well with that of measurement data using U-235 fission chamber, which was conducted at MK-I core start-up tests, except the stellite region. (3)As to the relative values of dose rate, calculation by "DOT3.5" and estimation by measured dose rate agree within factor 3 for the attenuation of 10
from bottom to sodium level of UGT. The above relative distribution agrees well with that of measurement data using U-235 fission chamber, which was conducted at MK-I core start-up tests, except the stellite region. (3)As to the relative values of dose rate, calculation by "DOT3.5" and estimation by measured dose rate agree within factor 3 for the attenuation of 10 . It is confirmed that the calculation can predict well the measurement. (4)Absolute amount of CP estimated by gamma spectra analysis and waste water analysis is 180 MBq.
. It is confirmed that the calculation can predict well the measurement. (4)Absolute amount of CP estimated by gamma spectra analysis and waste water analysis is 180 MBq.  Co dominates 92 % of CP. This value agrees with the prediction by corrosion product behavior analysis code "PSYCHE" within factor 2.
Co dominates 92 % of CP. This value agrees with the prediction by corrosion product behavior analysis code "PSYCHE" within factor 2.
; *; Furuhashi, Ichiro*
PNC TN9410 88-147, 215 Pages, 1988/09
The present study includes the analytical work for of the stable crack growth of the finite plate with semi-elliptical surface defect by creep-fatigue loadings, and of the crack opening area for presumed leakage of cloolant to be considered in safety assessment. The objective of this study is to develop the basic inelastic fracture mechanics to the level in which the integrity of basic components, plate, vessel, piping, and so on, with crack would be able to be assessed analytically. CANIS code developed last year was used to analize the J integral for fatigue crack growth and J' integral for creep crack growth of SUS 304 plates with various shapes of semi-elliptical surface cracks at 500  C, then those distributions were arranged from the view point of crack growth assessment. An appricable range of these data is
C, then those distributions were arranged from the view point of crack growth assessment. An appricable range of these data is  1.5 Sm of fatigue cycle and hold time of 10
1.5 Sm of fatigue cycle and hold time of 10 8,000 hr creep. 0nly secondary stress including membrane, bending and combination of these stresses were considered in the data base. Evaluation of elbow with 42
8,000 hr creep. 0nly secondary stress including membrane, bending and combination of these stresses were considered in the data base. Evaluation of elbow with 42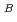 diameter and 20.6mm thickness considered in the design of large loop type FBR were achieved based on the data base. Then calculated through wall crack lengths were applied to the calculation of opening areas of 42
diameter and 20.6mm thickness considered in the design of large loop type FBR were achieved based on the data base. Then calculated through wall crack lengths were applied to the calculation of opening areas of 42 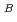 elbow subjected of internal pressure of 2 atg and in plane bending moment corresponding to stress level of 1.5Sm. The results are (1)A numbers of cycles at penetration are 6,250 for membrane stress and 30,520 for bending stress in the case of fatigue, and 303 for memberane and 1,534 for bending in the case of creep-fatigue. (2)opening area against internal pressure is larger than that against bending moment, and is about 0.5mm
elbow subjected of internal pressure of 2 atg and in plane bending moment corresponding to stress level of 1.5Sm. The results are (1)A numbers of cycles at penetration are 6,250 for membrane stress and 30,520 for bending stress in the case of fatigue, and 303 for memberane and 1,534 for bending in the case of creep-fatigue. (2)opening area against internal pressure is larger than that against bending moment, and is about 0.5mm . (3)maximum leak rate from the opening area is about 23
. (3)maximum leak rate from the opening area is about 23  /hr. The level up of analytical method for stable crack growth was almost accomplished. In the near future, the experimental study would be needed for validation of this method.
/hr. The level up of analytical method for stable crack growth was almost accomplished. In the near future, the experimental study would be needed for validation of this method.